From HowToGeek.com :
You are probably very familiar with the startup programs function of Windows. While you can specify the applications you want to launch at the start of Windows, the ability to control the order in which they start is not available. However, there are a couple of ways you can easily overcome this limitation and control the startup order of applications.
Note: this tutorial should work for any version of Windows, including Windows Server.
Using WinPatrol
There are most likely several utilities which provide this functionality, but we are going to discuss using the popular WinPatrol monitoring application which features a delay startup control. As you can probably guess, this function allows you to specify a certain amount of time to wait before opening the respective application.
WinPatrol makes this process very easy. On the Startup Programs tab, locate the applications you want to delay the startup for, right-click and select the “Move to Delayed Start Program List” option.

After selecting this option for all the target applications, click the Delayed Start tab. Here you can add additional applications manually and set the respective delay by highlighting the target entry and clicking “Delay Options”.

Now set the delay time and any respective parameters.

Since WinPatrol initiates the launch commands, the delay time is respective to when it opens. So, of course, you must have WinPatrol as a startup application itself (which is the application default).
Using a Batch Script
If you do not want to install or rely on “yet another application” or you simply want to get a bit geeky, a batch script can be used. Anyone can do this as it is very easy to setup and requires no batch programming knowledge.
Open your Windows Startup folder by going to Start > All Programs, right-click on the Startup folder and selecting Open.

When the listing of programs appear, create a new text file named “StartupOrder.bat”.

Edit the StartupOrder.bat file in Notepad to add the delay time and applications you want to launch. For this task, we will need the use of two batch commands: TIMEOUT and START.
The use of the TIMEOUT command is to specify the delay. Usage is simply this:
TIMEOUT /T seconds-to-wait
For example the following two commands would wait 10 seconds and 2 minutes (120 seconds), respectively, before continuing:
TIMEOUT /T 10
TIMEOUT /T 120
The use of the START command is to launch the target application. The reason we use the START command instead of just entering the program name is to tell the batch script to launch the target application and move on without waiting until we close it. Our usage of this command is:
START “” “C:PathToApplication.exe”
For example, the following two commands would open Notepad and the Calculator without waiting for the other to close (i.e. at the same time):
START “” “Notepad.exe”
START “” “Calc.exe”
Putting it Together
All you need to do to get your custom StartupOrder.bat script working it combine the delay (TIMEOUT) and launch (START) commands in the order you want them processed.
Here is the batch script which would implement the same startup delay we specified in the WinPatrol example above:
@ECHO OFF
TIMEOUT /T 10
REM Total Delay = 10 seconds
START “” “C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft OfficeOffice14OUTLOOK.EXE”
TIMEOUT /T 20
REM Total Delay = 30 seconds
START “” “C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft OfficeOffice14WINWORD.EXE”
START “” “C:Program Files (x86)CitrixGoToMeeting457g2mstart.exe”
TIMEOUT /T 20
REM Total Delay = 50 seconds
START “” “C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft OfficeOffice14EXCEL.EXE”
You can use this example to get you started and customize as needed.
How to add Google documents to the windows explorer menu… follow the faq on HowToGeek.com
From labo-microsoft.org :
« …Bitlocker est une technique de chiffrement de lecteur qui est utilisée pour sécuriser vos données par mot de passe. Les données sont cryptées à l’aide d’un algorithme de chiffrement fort ce qui vous confère une sécurité maximale. Bitlocker Drive Encryption encrypte vos données de sorte que même si votre système d’exploitation n’est pas démarré les données sont cryptées, c’est-à-dire que si vous vous faites voler votre DD les données contenues par celui-ci sont illisibles ou inaccessibles. Il est possible de crypter plusieurs supports tels qu’un disque dur interne, un disque dur externe ou une clé USB grâce à Bitlocker to Go. Cette nouveauté est arrivée avec Windows… »
From SupportMicrosoft.com :
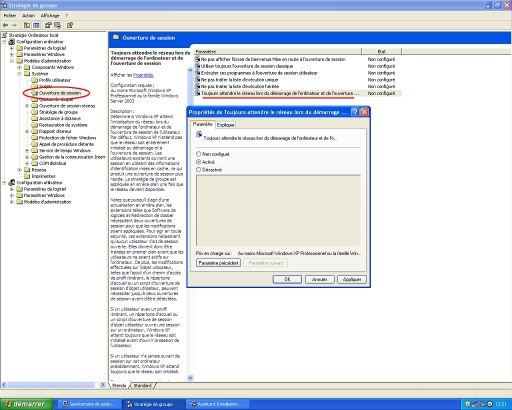
« … By default in Windows XP Professional, the Fast Logon Optimization feature is set for both domain and workgroup members. As a result, Windows XP does not wait for the network to be fully initialized at startup and logon.
From Kixtart.org :
The logon optimization can be disabled in the following ways:
- Local PO via « Computer ConfigurationAdministrative TemplatesSystemLogonAlways wait for the network at computer startup and logon »
- Global PO via « Computer ConfigurationAdministrative TemplatesSystemLogonAlways wait for the network at computer startup and logon »
- Per-machine registry hack as a policy via « HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionWinlogon » with registry value « SyncForegroundPolicy »=dword:00000001
- Per-machine registry hack via « HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionWinlogon » with registry value « SyncForegroundPolicy »=dword:00000001
- Per-user registry hack as a policy via « HKEY_CURRENT_USERSOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionWinlogon » with registry value « SyncForegroundPolicy »=dword:00000001
- Per-user registry hack via « HKEY_CURRENT_USERSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionWinlogon » with registry value « SyncForegroundPolicy »=dword:00000001
Fron HowToGeek

Anytime somebody has hard drive errors, I always recommend that they run chkdsk—what geek wouldn’t? Here’s a full guide to using the Check Disk feature built into every version of Windows.
The chkdsk or “Check Disk” utility is used in Windows to scan through your entire hard drive and find problems… it’s like a lot like doing inventory… it’s boring, but it has to be done sometimes. I recommend that you run through a check disk every month or two.
Image by Nemo
Using CheckDisk the GUI Way
Open up Computer and then right-click on the drive you want to check, and choose Properties, or just click the drive, and then click the Properties button.

Then select the Tools tab, and click the “Check Now” button.

A little dialog will pop up to allow you to choose the options you want for the disk check. You should check both options if you want to really check the disk properly, but if you just want to do a quick check you could select only the first one.

The only problem with that is that Windows can’t check a drive that’s being used, such as the system drive, but Windows will let you schedule a disk check for the next reboot.

You should keep in mind that running through a full check disk takes quite a while, sometimes hours depending on how big the drive is and how many files you have.
Cancelling the Scheduled Disk Check
If you had scheduled a disk check but decided you would like to cancel it, you can run a command to
Open up an administrator mode command prompt by right-clicking on the item in the start menu and choosing “Run as Administrator”. Type in the following command, substituting the drive letter if necessary.
chkntfs /x c:

Seems like they could have a better command line output… something like “canceled!” would have even worked… oh well.
How to Tell if a Manual Disk Check is Scheduled
Open an admin mode command prompt, and then type in the following command:
chkntfs c:

How to Tell if an Automatic Disk Check is Scheduled
Sometimes if your computer has not shut down correctly, Windows will mark the drive as “dirty” basically as a reminder to itself that the drive probably has filesystem errors and should be checked. When the flag is set, you’ll be told the disk requires checking during the next bootup.
You can easily see the state of this flag by using two different command line options. The first is the same command as above, but you can see the output is different if the drive is set to be automatically checked.
chkntfs c:

You could also use this command to just query the dirty bit:
fsutil dirty query c:

Using CheckDisk from the Command Line
Open up an administrator mode command prompt, and then type in the following command to do an exhaustive check of your drive. Substitute C: for whatever drive you want to check.
chkdsk /f /r C:
If the drive is a system drive or has files in use, you’ll be asked to schedule the check for the next reboot:

The above command is the recommended way to perform a disk check, but if you want to do a less exhaustive check, you could remove the /R option from the command.
Here’s the full list of parameters for your geeky enjoyment:
C:>chkdsk /?
Checks a disk and displays a status report.
CHKDSK [volume[[path]filename]]] [/F] [/V] [/R] [/X] [/I] [/C] [/L[:size]] [/B]
volume Specifies the drive letter (followed by a colon),
mount point, or volume name.
filename FAT/FAT32 only: Specifies the files to check for fragmentation.
/F Fixes errors on the disk.
/V On FAT/FAT32: Displays the full path and name of every file
on the disk.
On NTFS: Displays cleanup messages if any.
/R Locates bad sectors and recovers readable information
(implies /F).
/L:size NTFS only: Changes the log file size to the specified number
of kilobytes. If size is not specified, displays current
size.
/X Forces the volume to dismount first if necessary.
All opened handles to the volume would then be invalid
(implies /F).
/I NTFS only: Performs a less vigorous check of index entries.
/C NTFS only: Skips checking of cycles within the folder
structure.
/B NTFS only: Re-evaluates bad clusters on the volume
(implies /R)
The /I or /C switch reduces the amount of time required to run Chkdsk by
skipping certain checks of the volume.
Note: You’ll probably notice that this guide was originally written a few years ago. We’ve updated it for Windows 7 and are republishing it for all the readers that might have missed it the first time.
From Labo-microsoft.org :
« … DISM est l’acronyme de « Deployment Image Servicing and Management » qui peut se traduire par « Gestion et services pour le déploiement d’images ».
Cet outil va nous permettre de créer des images personnalisées qui serviront ensuite, soit à les déployer via WAIK (Windows Automated Installation Kit) et/ou MDT (Microsoft Deployment Toolkit), soit à refaire des supports d’installation.
Le principal intérêt de DISM est qu’il est présent directement dans toutes les éditions de Windows 7 ! Il n’est pas nécessaire de télécharger quoi que ce soit d’autre. De plus, DISM est un outil en lignes de commandes, ce qui permet la création de scripts automatisés (en Batch par exemple)… »
Copssh is an ssh server and client implementation for windows systems. It is a yet another packaging of portable openssh, cygwin, some popular utilites, plus implementation of some best practices regarding security. You can use copssh for remote administration of your systems or gathering remote information in a secure way.
OpenSSH is a FREE version of the SSH protocol suite of network connectivity tools. It encrypts all traffic (including passwords) to effectively eliminate eavesdropping, connection hijacking, and other network-level attacks. Additionally, OpenSSH provides a myriad of secure tunneling capabilities, as well as a variety of authentication methods. Cygwin is a Linux-like environment for Windows. It consists of a DLL (cygwin1.dll), which emulates substantial Linux API functionality, and a collection of tools.
Comparaison des clients SSH
From http://www.howtogeek.com
Will your computer not boot into Windows after installing an update on your dual-boot or Wubi Ubuntu install? Here’s how you can get your Windows boot loader back so you can easily get back to work in either OS.
We’ve mentioned before how Wubi is a great way to run Ubuntu on your Windows PC or netbook, and in general it works great. However, sometimes your system may receive updates to GRUB, and if you choose the wrong option, the next time you reboot your computer you may find that it think there’s only Ubuntu and no Windows installed on your computer.

Or, perhaps, even more ominously, you boot your computer to see that it thinks it has no operating system.

Often, there’s no need to panic. If you recently received an Ubuntu update, or somehow managed to mess up or remove your boot loader, it’s quick and easy to get it back using familiar Windows tools. Here’s how.
Reinstall Your Windows Boot Loader From the Windows DVD
To get back into Windows, you’ll need to reinstall your Windows boot loader. Thankfully this isn’t as difficult or time consuming as reinstalling Windows, but it will require your Windows DVD. Boot your computer from the DVD, and if it doesn’t automatically offer to let you boot from the disk, you may need to change your boot settings in the BIOS. You can usually access by pressing the F2, F10, or Delete key on the initial boot screen, depending on your computer.

Save the changes and reboot your computer from the Windows DVD. After a few moments, you should see the install setup screen. Select your preferred language, then click Next.

Your install disk is designed to install Windows on your computer, but also contains tools to help repair your existing Windows install. On the bottom left of the Install window, click the Repair your computer link to get started repairing your current install of Windows.

System Recovery will automatically start scanning to see if there’s an existing Windows install with something it can easily fix automatically. You may have to wait a few minutes while it scans your computer.

If your only problem is the boot loader, often it will automatically detect the problem and offer to fix it. If so, simply click Repair and restart, and your computer should be booted back into Windows as normal within minutes.

Reinstall Your Boot Loader Manually From the Windows DVD
Alternately, if it doesn’t automatically detect anything to fix, you’ll have to choose your own recovery options. Click the bullet option on the top then click Next to use recovery tools to fix Windows.

Now, select Command Prompt from the available recovery tools.

In the command prompt window, enter the following to repair your boot loader:
bootrec /rebuildbcd
After a few moments, it should detect your Windows installation and ask if you want to add it to the boot loader. Enter Y to add it, then exit the command prompt and reboot your computer when you’re finished.

Moments later, you should see your standard Windows login screen as normal, and all of your files and programs should be fine and ready to use.

As you may notice, the option to boot into Ubuntu will no longer show up in your boot menu, and your computer will act like you only have Windows installed. To get your Wubi Ubuntu or full Ubuntu install accessable from the boot loader again, you’ll need to restore it as well. The easiest way is to Add Wubi Back to the Bootloader With EasyBCD. Once you’ve done that, you should be back in business, ready to use Windows or Ubuntu as you need.
From http://www.howtogeek.com

Ever need to grab a file or two from your ext4 partition? Maybe you’ve wanted to backup a few important files while you were in Windows. Here’s how to browse your Linux partition from Windows using a tool called Ext2explore.
Most Linux distributions nowadays use the ext4 partition by default, and while there are some tools that can read the older ext2 and ext3 partitions, Ext2explore (also known as Ext2Read) is the only one that we’ve seen that is able to read all three. In the spirit of Linux, it’s also open source.
You can download Ext2explore from the Ext2Read Sourceforge page, and runs on Windows XP SP3, as well as Vista and 7 in compatibility mode.
There is no installation for the utility, so just unzip the file. You can give it its own folder, if you like. Ext2explore has a few compatibility issues, so let’s fix them first, shall we? Right-click the .exe file and go to Properties.

Then, click on the Compatibility tab.

Under “Compatibility Mode” choose Windows XP (Service Pack 3) from the drop-down menu. Next, check the Run this program as an administrator item, and click OK. This insures that the program runs smoothly (we had no issues with the XP SP3 setting) and has the privileges to access unmounted partitions.
Just double-click the program to launch it. You’ll get a security warning from Windows, to which you should respond Yes.

You should see the main Ext2explore window:

The program automatically scans your disks for ext partitions. This also works on USB disks, too! If nothing is shown or you get an error message stating no ext partitions were found, verify that ran the program as an administrator, and rescan by clicking the computer monitor icon in the top bar (next to Tux the penguin).

Double-click on folders to open them, and navigate around like you would in Explorer. You can view files’ properties, or save them to another folder on your Windows partition by right-clicking and selecting Save.

You’ll see a prompt asking you where to save your chosen files/folders to.

You’ll see a “Saving…” dialog and there you go!

While you won’t be able to write to ext2, ext3, or ext4 partitions, this is a great utility that can save you in a pinch if you just need a few files from your Linux partition. It’s also not a bad way to backup some important things if your Linux install fails to boot, though be careful with file permissions once you’re back in Linux.
Merci Loig
« …Pendant la procédure d’installation sur les poste client SEVEN, je désactive l’ipv6 via les propriétés de la « connexion réseau ». Cela ne désactive pas totalement l’ipv6, il faut aussi rajouter une valeur dans la base de registre :
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesTCPIP6Parameters]
"DisabledComponents"=dword:ffffffff
****************
"DisabledComponents"=dword:0 -> Active tous les composants
ipv6
"DisabledComponents"=dword:ffffffff -> Désactive tous les
composants ipv6
"DisabledComponents"=dword:20 -> Utilise ipv4 au lieu de ipv6
"DisabledComponents"=dword:10 -> Désactive les interface ipv6
natifs
"DisabledComponents"=dword:01 -> Désactive toutes les
interface tunnel
...
****************
NB : il est possible de modifier la base de registre en mode silencieuse.
" C:>reg import ipv6.reg " ou avec " C:>reg add ...".